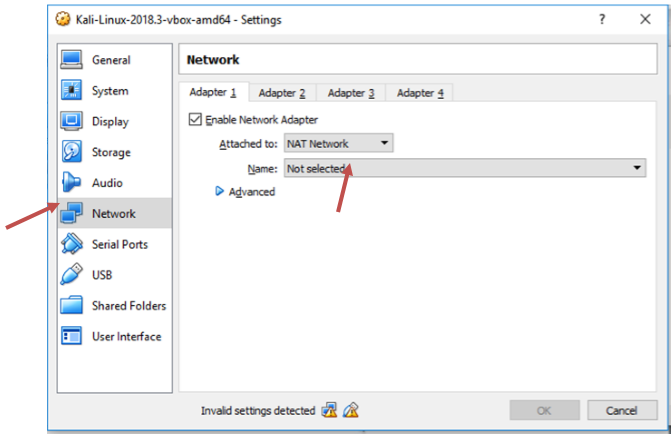
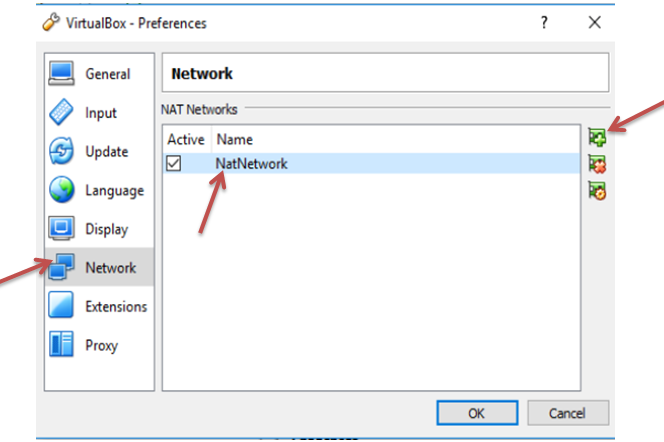
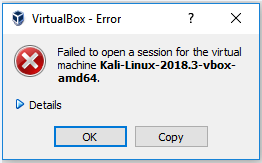
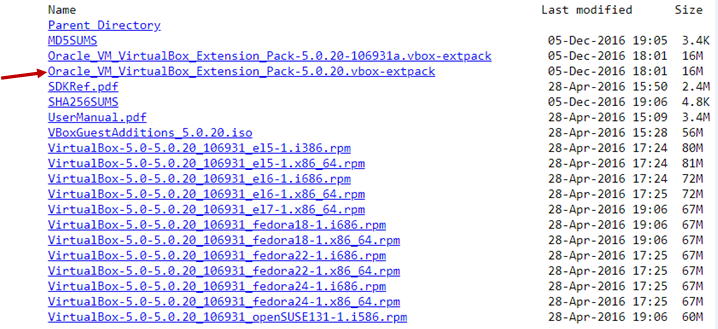
Famous Hackers
In this section, we will see some of the famous hackers and how they become famous.
Jonathan James
Jonathan James was an American hacker. He is the first Juvenile send to prison for cybercrime in the United States. He committed suicide on 18 May 2008, of a self-inflicted gunshot wound.
In 1999, at the age of 16, he gained access to several computers by breaking the password of a NASA server and stealing the source code of the International Space Station, including control of the temperature and humidity within the living space.
Kevin Mitnick
He is a computer security consultant, author, and hacker. He infiltrates his client's companies to expose their security strengths, weaknesses, and potential loopholes. In the history of the United state, he was formerly the most wanted computer criminal.
From the 1970s up until his last arrest in 1995, he skillfully bypassed corporate security safeguards and found his way into some of the most well-guarded systems like Sun Microsystems, Nokia, Motorola, Netcom, and Digital Equipment Corporation.
Mark Abene
Mark Abene is an American Infosec expert and Entrepreneur. He is known around the world by his pseudonym Phiber Optik. Once, he was a member of the hacker groups Legion of Doom and Master of Deception. He was a high-profile hacker in the 1980s and early 1990s.
He openly debated and defended the positive merits of ethical hacking as a beneficial tool for the industry. He is also an expert in penetration studies, security policy review and generation, on-site security assessments, systems administration, and network management, among many others.
Robert Morris
Robert Morris was the creator of the Morris Worm. He was the first computer worm to be unleashed on the Internet. The Morris Worm could slow down computers and make them no longer usable. Due to this, he was sentenced to three years probation, 400 hours of community service, and also had to pay a penalty amount of $10,500.
Gary McKinnon
Gary McKinnon is a Scottish systems administrator and Hacker. In 2002, he was accused of the "biggest military computer hack of all time". He has successfully hacked the network of the Navy, Army, Air Force, and NASA systems of the United States Government.
In his statement to the media, he has often mentioned that his motivation was only to find evidence of UFOs and the suppression of "free energy" that could potentially be useful to the public.
Linus Torvalds
Linus Torvalds is a Finnish-American software engineer and one of the best hackers of all time. He is the developer of the very popular Unix-based operating system called Linux. Linux operating system is open source, and thousands of developers have contributed to its kernel. However, he remains the ultimate authority on what new code is incorporated into the standard Linux kernel.
Torvalds just aspires to be simple and have fun by making the world's best operating system. Linus Torvalds has received honorary doctorates from the University of Helsinki and Stockholm University.
Kevin Poulsen
Kevin Poulsen is an American former Black-hat hacker. He is also known as Dark Dante. He took over all the telephone lines of radio station KIIS-FM of Los Angeles, guaranteeing that he would be the 102nd caller and win the prize of a Porsche 944 S2.
Poulsen also drew the ire of the FBI, when he hacked into federal computers for wiretap information. As a result of this, he was sentenced to five years. He has reinvented himself as a journalist.